Longevity Science
According to current studies, the combination of NMN and resveratrol enhances the longevity effect by increasing NAD+ levels and supporting the activity of sirtuins. This synergy maximizes cellular repair processes while promoting healthy aging.
The Synergy of Resveratrol and NMN: Key to Cellular Health and Longevity
Since the beginning of human history, we have been trying to unravel the secrets of life. While our ancestors primarily investigated the visible, our modern gaze is increasingly focused on the invisible molecules that work in every cell. Two such fascinating molecules that have increasingly become the focus of research in recent years are resveratrol and nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN). Together they form a powerful alliance that intervenes deeply in the biochemical processes of longevity. Come with us on a journey into the world of biochemistry, where these two molecules appear as central players in cellular health and energy production.
As cells derive energy from food, NAD+ acts as an essential co-factor in the conversion of nutrients into energy. NMN serves as a precursor to NAD+, while resveratrol activates the sirtuins responsible for protecting and repairing cells. Together, they support cellular health, promote DNA repair, and counteract age-related declines in these vital processes.
Before we delve deeper into the subject, let us first take a closer look at some of these technical terms.
What is an enzyme?
What is an enzyme?
Similar to hormones and antibodies, enzymes are made of proteins, the basic building blocks of life.
In our bodies, countless enzymes act as biocatalysts every second to control a variety of biological processes. This function is similar to that of catalysts in vehicles: they are substances that can influence the rate of chemical reactions without themselves being consumed. Simply put, enzymes allow biological reactions to take place under less demanding conditions.
The breakdown of substances by enzymes is called catabolism, whereby complex molecules are converted into simpler ones. On the other hand, enzymes can also be involved in the construction of substances, a process known as anabolism. A prominent example of this is the enzyme ATP synthase (adenosine triphosphate synthase), which typically ends in -ase and, together with NAD+, plays a crucial role in the energy supply in living organisms.
What is NAD+ and what is a coenzyme?
What is NAD+ and what is a coenzyme?
NAD+ stands for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, with the plus sign symbolizing a positive electrical charge. It is a coenzyme that is found in almost every cell in the body. Coenzymes are small organic molecules that are essential for activating enzymes and thus for starting chemical reactions. An appropriate NAD+ level is of great importance for many cellular processes. However, the amount of NAD+ decreases over time, which is rather detrimental to the organism.
NAD+ is formed in the body by synthesis from certain precursors, a process that occurs via three different pathways. A simplified representation of the three synthesis pathways includes the "de novo" pathway, which begins with tryptophan as the starting material, the "Preiss-Handler" pathway, which uses niacin as a base, and the "salvage pathway," which allows NAD to be recycled in the body. "Salvage" means something like "to salvage" or "to save." In this context , nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) plays a key role.
NMN acts as the central precursor molecule for NAD in the salvage pathway. This means that NMN is an essential intermediate for the synthesis of NAD from other precursors such as nicotinamide riboside (NR) or nicotinamide (Nam). This makes NMN essential for maintaining and restoring NAD levels in the body. Let's take a closer look at this crucial molecule.
What is NMN?
What is NMN?
NMN, short for nicotinamide mononucleotide , is a derivative of vitamin B3 and plays a central role in the biosynthesis of NAD+ in all living organisms.
NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) is a coenzyme involved in a variety of cellular processes, particularly in energy metabolism and DNA repair. Since NAD+ declines with age, NMN is considered a potential agent to increase NAD+ levels and is therefore an important area of research in anti-aging and longevity.
What is Resveratrol?
What is Resveratrol?
Resveratrol is a plant polyphenol found primarily in grapes, berries and nuts and is known for its antioxidant properties. It plays a key role in protecting cells from oxidative stress and inflammation associated with aging and degenerative diseases.
In addition, resveratrol supports the activation of sirtuins, proteins that play a role in regulating cell metabolism and DNA repair. Due to these effects, it is being intensively studied in the field of longevity and anti-aging research.

Effects of NMN Supplementation
Several preclinical studies have shown that NMN supplementation effectively increases NAD+ levels in various organisms, including mice and humans:
- Improved mitochondrial function : Studies in mice have shown that NMN improves mitochondrial functions by increasing ATP production and reducing oxidative stress.
- Delaying age-related diseases : NMN has shown positive effects on age-related diseases such as type 2 diabetes, neurodegenerative diseases and cardiovascular problems in animal studies.
- Human Studies : Initial clinical studies in humans have shown that NMN is safe and can significantly increase NAD+ levels in tissues, leading to improved physical endurance and potentially slowing the aging process.
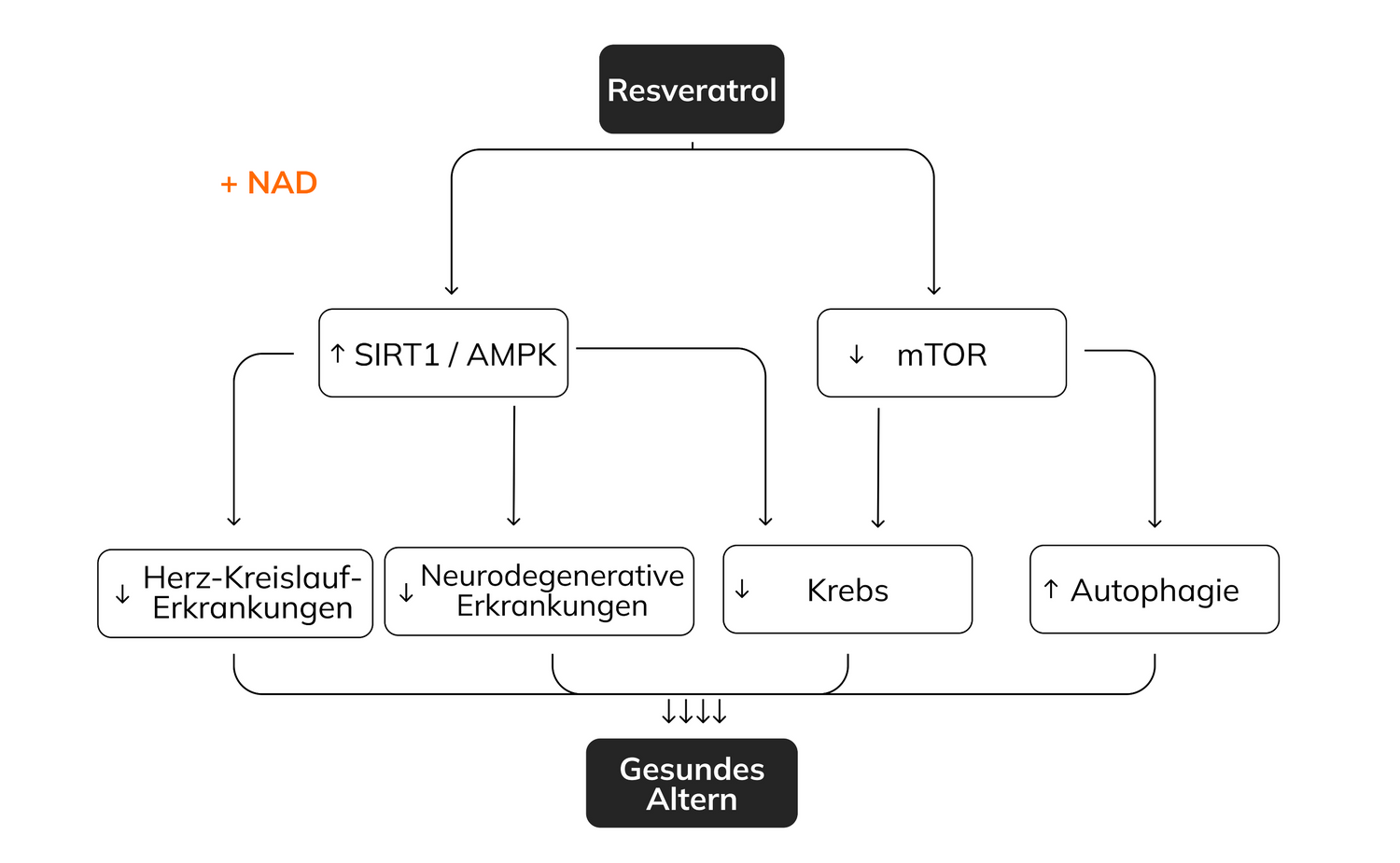
Effects of Resveratrol
Resveratrol helps plants fight injury by acting as a stress messenger. It is thought that resveratrol may also act as a stress signal in humans, similar to the physiological stress induced by physical activity or calorie restriction. This type of stress appears to be beneficial, as both exercise and calorie restriction have been shown to have positive effects on longevity. In studies, resveratrol has been shown to extend the lifespan of various organisms, including yeast, worms, and fish. It was also found to reduce the risk of death by 30% in mice fed an unhealthy diet. However, whether resveratrol can produce similar effects in healthy mammals, including humans, remains to be confirmed.
Similar to exercise and calorie restriction, resveratrol activates the enzyme SIRT1 , which has been called the "longevity protein." Resveratrol binds to SIRT1 and increases its sensitivity to NAD+ , thereby increasing the efficiency of NAD+ utilization. This synergistic effect of NAD+ and resveratrol suggests that combined supplementation could potentially provide additive health benefits.
In addition to activating the sirtuin pathway, resveratrol also affects the mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) pathway . mTOR is known to inhibit autophagy - a cellular process that is crucial for the degradation and elimination of damaged cellular components. Resveratrol inhibits the activity of mTOR, thereby promoting autophagy. This mechanism plays an important role in the aging process and is central to the prevention of diseases such as cancer.
The synergistic effect of NMN and resveratrol
Although NMN and resveratrol offer significant benefits independently, when combined they greatly enhance their effects. A key mechanism here is the close connection between NAD+ and sirtuins: sirtuins are NAD+-dependent enzymes, meaning their activity is highly dependent on NAD+ levels in the body.
Resveratrol activates the sirtuins, but without sufficient NAD+ they remain inactive. This is where NMN comes in to help: by increasing the NAD+ levels, it ensures that the sirtuins can develop their full effect.
In studies with mice, the combined administration of NMN and resveratrol was shown to improve metabolic and cellular functions more effectively than was possible with individual use. This synergy not only promotes mitochondrial health and energy production, but also contributes to DNA repair and the reduction of oxidative stress, which significantly contribute to delaying the aging process.
In addition, there is evidence that the combination of both molecules supports blood vessel regeneration and endothelial function, which is particularly crucial for cardiovascular health. These synergistic effects have the potential to counteract degenerative diseases of aging such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes and neurodegenerative diseases.
Longevity Bundle
Longevity Bundle
✓ The two top innovations from beLIVELY in the advantage bundle
✓ High-quality raw materials with premium quality
✓ Contents: 60g NMN ( nicotinamide mononucleotide ), 50g resveratrol
✓ Purity certified in independent German laboratories
content and size
content and size
filling quantity
- NMN: 60g
- Resvertrol: 50g
recommended dosage
recommended dosage
NMN: 1-2 scoops (500 - 1000 mg) per day. Dissolve powder under the tongue.
Resveratrol: 1 scoop (500 mg) per day. Take with a meal.













