What is NMN?
For countless generations, we have striven to unravel the mysteries of biochemical processes. While our ancestors focused on phenomena they could see with their own eyes, today our gaze is increasingly directed towards the molecular level. We are constantly discovering new molecules on the horizon of science, which we try to fit into the existing schemes of biochemistry and biology. One such rising star in this universe of molecules is nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) , a molecule that has become increasingly the focus of research in recent years. Come with us on an accessible journey of discovery into biochemistry as we take a closer look at NMN, a leading player in the realm of NAD.
The world of organisms is breathtakingly complex, with countless processes taking place in fractions of a second. All of these processes are based on one elementary building block: energy. Organisms obtain energy from food, which is broken down into its basic components and ultimately assimilated. Similar to the conversion of solar heat into electricity, molecules must also be converted into a usable form of energy at the cellular level. This essential conversion takes place in the mitochondria, the energy centers of the cell. There, the enzyme ATP synthase produces adenosine triphosphate (ATP), a universal and immediately available energy carrier in cells and thus in the entire organism. ATP synthase is supported by NAD+, an essential cofactor. NMN serves as a precursor to NAD+ and thus plays a key role in this energetic cycle. Before we delve deeper into the matter, let's first take a closer look at some of these technical terms.

Search results for “NMN” on PubMed by calendar year. Interest in the topic is increasing rapidly.
What is an enzyme?
Much like hormones and antibodies, enzymes are made of proteins, the basic building blocks of life. In our bodies, countless enzymes act as biocatalysts every second to control a variety of biological processes. This function is similar to that of catalysts in vehicles: they are substances that can influence the rate of chemical reactions without themselves being consumed in the process. Simply put, enzymes allow biological reactions to occur under less demanding conditions. The breakdown of substances by enzymes is called catabolism, where complex molecules are converted into simpler ones. On the other hand, enzymes can also be involved in the building of substances, a process called anabolism. A prominent example of this is the enzyme ATP synthase (adenosine triphosphate synthase), which typically ends in -ase and, together with NAD+, plays a crucial role in the energy supply in living organisms.
What is NAD+ and what is a coenzyme?
NAD+ stands for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, with the plus sign symbolizing a positive electrical charge. It is a coenzyme that is found in almost every cell in the body. Coenzymes are small organic molecules that are essential for activating enzymes and thus for starting chemical reactions. An appropriate NAD+ level is of great importance for many cellular processes. However, the amount of NAD+ decreases over time, which is rather detrimental to the organism.
NAD+ is formed in the body by synthesis from certain precursors, a process that occurs via three different pathways. A simplified representation of the three synthesis pathways includes the "de novo" pathway, which begins with tryptophan as the starting material, the "Preiss-Handler" pathway, which uses niacin as a base, and the "salvage pathway," which allows NAD to be recycled in the body. "Salvage" means something like "to salvage" or "to save." In this context , nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) plays a key role.
NMN acts as the central precursor molecule for NAD in the salvage pathway. This means that NMN is an essential intermediate for the synthesis of NAD from other precursors such as nicotinamide riboside (NR) or nicotinamide (Nam). This makes NMN essential for maintaining and restoring NAD levels in the body. Let's take a closer look at this crucial molecule.

NMN in powder form
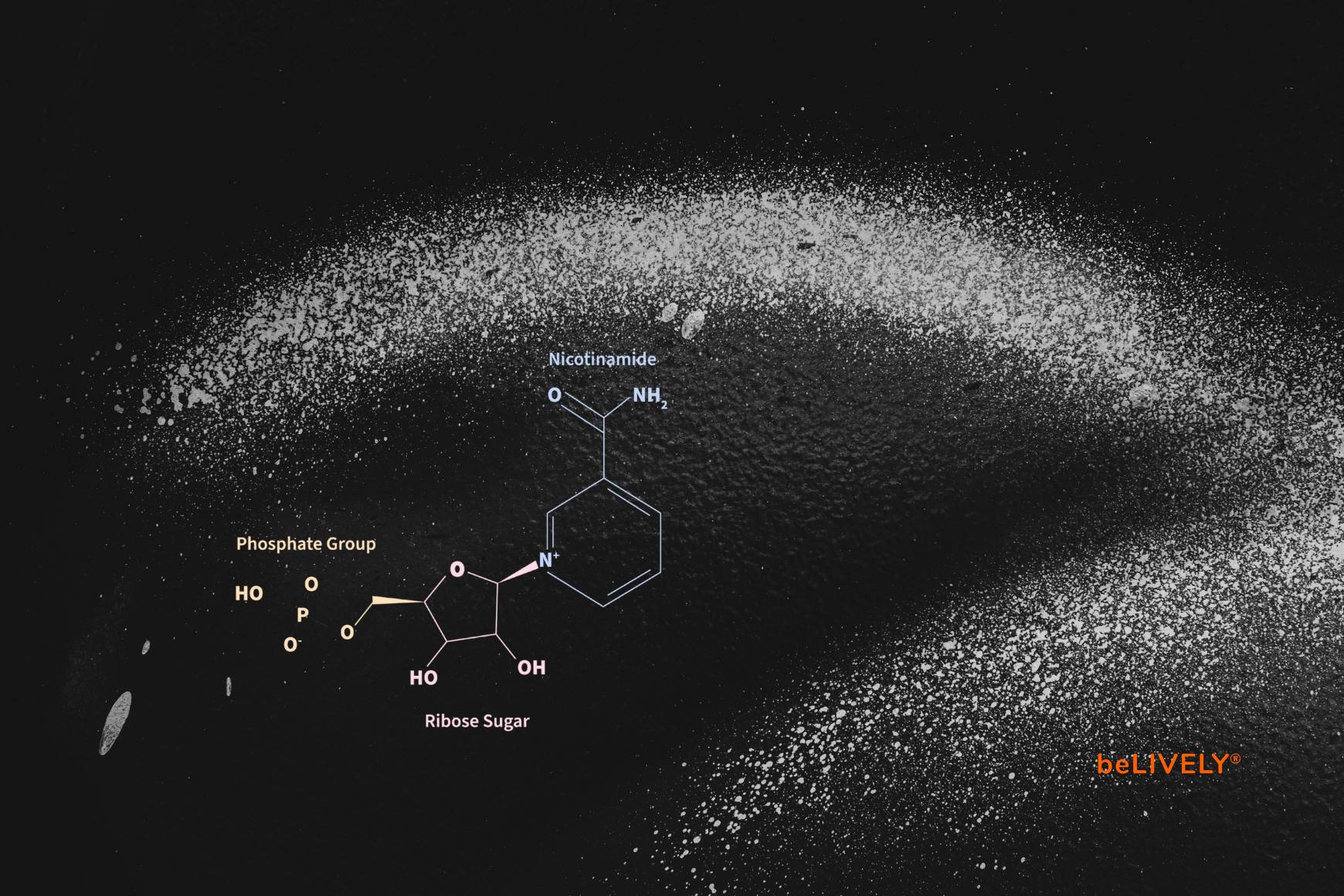
What is NMN?
NMN, short for nicotinamide mononucleotide , is a derivative of vitamin B3 and plays a central role in the biosynthesis of NAD+ in all living organisms. The chemical production of NMN is a particularly complex and costly process because it mimics the natural conversion of nicotinamide riboside (NR) to NMN. Due to these production challenges and the fact that NMN is currently used exclusively in research, the molecule is relatively expensive. It is therefore not surprising that NMN is one of the most counterfeited substances in the world.
A recent study conducted in the US that examined 22 different NMN suppliers revealed disappointing results. More than half of the products tested did not contain authentic NMN or were of inferior quality. Click here to read the study
How can I recognize real NMN?
There are several approaches to reliably identify genuine NMN:
-
Have laboratory tests carried out: Although this is one of the most reliable methods, it is also expensive. Prices for such tests can vary between 150 and 300 euros depending on the laboratory. A purity level below 99% is considered unsatisfactory compared to the industry standard.
-
Check for the presence of certificates of analysis: Manufacturers offering genuine NMN should be able to provide current certificates of analysis. The absence of such certificates is often an indicator of inauthentic NMN. The relevant certificates for all tested batches can be found in the product information section on our website.
-
Pay attention to the consistency of the product: NMN is characterized by a fluffy and loose consistency. With prolonged pressure, slight clumping may occur, but this does not affect the quality of the product.
-
Price evaluation: Despite falling prices in recent years, NMN remains a relatively expensive molecule. Products that are offered at a strikingly low price should be treated with caution. A price comparison based on the price per gram can be helpful here.
In summary, trust is valuable, but thorough verification is essential. Reputable suppliers are aware of the problem with fake NMN and are happy to provide the necessary documents for verification.
What does NMN do?
As we already know, acts as an immediate precursor to NAD+. Its role is crucial in the process of cellular respiration, a process that takes place in the mitochondria and without which life as we know it would not exist. This is because cellular respiration is the primary source of energy in organisms. Although alternative mechanisms for generating energy exist, they are not sufficient to meet the necessary energy needs in the long term. In addition, NAD+ plays an important role in interacting with genes that serve as instructions for protein production. Through this interaction, NAD+ promotes the activation of genes responsible for the production of sirtuins, an important family of genes.
Measuring NMN correctly
The dosage of nicotinamide mononucleotide, which is mostly available in powder form, often raises questions regarding the correct measurement.
Here are some practical methods:
-
Using a precision scale: For those who want to dose NMN with milligram precision, purchasing a precision scale is a good choice. There are already fairly accurate models on the market, available for around 10 to 15 euros. Of course, for laboratory-intensive work, a specialized laboratory scale is preferable.
-
Use of the beLIVELY beSCOOP: The beSCOOP has a volume of 1ml, which, depending on how the powder is stored, corresponds to about 400 to 500mg of NMN.
-
Measuring with a conventional teaspoon: A conventional teaspoon, leveled, has a volume of 3 to 5 ml. This corresponds to an amount of up to 2.5 grams of NMN powder.
research on NMN
Current research activities are focused on the study of NMN, which is currently used mainly as a research chemical in the life sciences. To gain an insight into the ongoing studies, here are some relevant publications dealing with NMN. For more detailed information, please see the links below to PubMed, a comprehensive database of medical literature in English.
- Study 1 on PubMed
- Study 2 on PubMed
- Study 3 on PubMed
- Study 4 on PubMed
- Study 5 on PubMed
- Study 6 on PubMed
It will be exciting to see what results future scientific research will produce and how knowledge about this molecule will develop. It is important to stay on the ball of science in order to gain new insights and possibly revise existing knowledge. History has shown that the quest for understanding the fundamental processes in living organisms is tireless - and this will not change in the future.



4 comments
Da NMN einen Energieschub verleihen kann, empfiehlt sich die Einnahme am Morgen.
Spielt es eine Rolle, zu welcher Tageszeit ich die Kapsel einnehme?
Laut Herstellern ist das die beste Art: Die wirksamste Art, NMN aufzunehmen, ist die sublinguale Einnahme, bei der das NMN unter die Zunge gelegt wird und über die Schleimhäute aufgenommen wird. Es wird empfohlen, bis zum Alter von 50 Jahren 500 mg (1 Dosierlöffel) einzunehmen. Ab dem 50. Lebensjahr wird eine Dosis von 1000 mg pro Tag (2 Dosierlöffel) empfohlen. Nach der Einnahme kann mit einem Schluck Wasser nachgespült werden.
wie nehme ich NMN Pulver ein? In wasser einen Teelöffel auflösen?